What is CMMC?
The Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) is a framework developed by the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) under DFARS Case 2019-D041 to ensure that contractors and other organizations that handle DoD information have appropriate safeguards in place to protect that information from cyber threats.
Under the CMMC, contractors must undergo a certification process to demonstrate that they have implemented the required security controls and practices.
Failure to obtain certification may result in the loss of existing contracts and the inability to bid on future contracts.
The CMMC is intended to improve the security of DoD information and protect against potential cyber threats. By requiring contractors to implement appropriate security controls and practices, the DoD hopes to reduce the risk of data breaches and other cybersecurity incidents.
Who is Impacted?
The CMMC applies to organizations in the Defense Industrial Base (DIB), which includes contractors and other organizations that do business with the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD).
Organizations that are impacted:
- The Defense Logistics Agency (DLA)
- Any other agencies within the DoD
In order to bid on and participate in certain DoD contracts, these contractors will be required to obtain CMMC certification. This means that they must implement the required security controls and practices and undergo a certification process to demonstrate their compliance. Failure to obtain certification may result in the loss of existing contracts and the inability to bid on future contracts.
CMMC Timeframe
The timeline for becoming CMMC compliant depends on several factors, including the level of compliance that an organization currently has and the level of CMMC certification that it is aiming for. Contractors are likely looking at September 2023 to be the earliest possible date for the CMMC rule to become final. No date has been officially set.
In general, organizations will need to implement the required security controls and practices and undergo a certification process to demonstrate their compliance. This process can take some time and may require the assistance of certified third-party assessment organizations (C3PAOs).
Under the current “interim rule,” defense contractors that process, store, or create Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) are required to submit a NIST 800-171 self-assessment and submit their score until CMMC is fully implemented. If the government decides that a further assessment is necessary, defense contractors must grant access to their facilities, systems, and employees.
The CMMC has become an official Defense Department policy, and the interim rule provides a timeline for compliance. An increasing number of contracts will formally require CMMC compliance in the Fall of 2025 when it will become a default requirement for all DoD contracts.
Prep Work
Organizations should familiarize themselves with CMMC requirements under the interim rule and prepare to apply for certification at a later date. Due to the low number of C3PAOs currently available, most organizations will be unable to receive the third-party assessment required for CMMC certification at this time.
CMMC Security Levels
The Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) has five security levels, each representing a different level of cybersecurity maturity. These levels are designed to provide organizations with flexibility in terms of their security practices and to recognize the different security needs and capabilities of organizations within the Defense Industrial Base (DIB).
The Three levels of CMMC are:
Level 1: Basic Cyber Hygiene
Level 2: Good Cyber Hygiene
Level 3: Advanced/Progressive
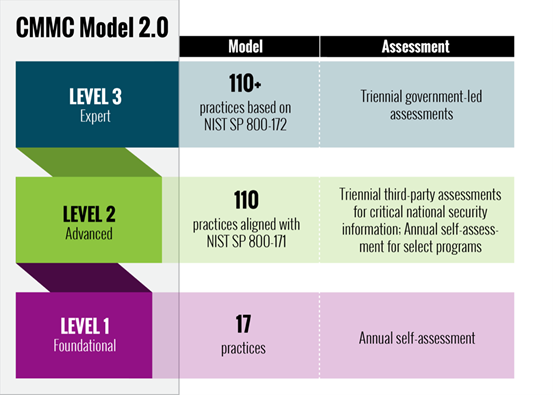
- Level 1 – Organizations are required to implement good cybersecurity practices, including the use of security policies and procedures, incident response plans, and data protection measures.
- Level 2 – Organizations are required to implement proactive cybersecurity practices, including the use of advanced security technologies and practices, such as encryption and network segmentation.
- Level 3 – Organizations are required to implement advanced and progressive cybersecurity practices, including the use of cutting-edge security technologies and practices to protect against sophisticated cyber threats.
In order to obtain CMMC certification, organizations must demonstrate that they have implemented the required security controls and practices for the level of certification that they are seeking. This will typically involve using a Registered Practitioner Organization (RPO) such as NOVO to assist with meeting the requirements and then undergoing a third-party assessment by a certified third-party assessment organization (C3PAO).
Challenges in Becoming CMMC Compliant
There are several challenges that organizations may face when trying to become CMMC compliant. These include:
- A lack of awareness and understanding of CMMC requirements: Many organizations may be unaware of the requirements of CMMC and may not understand what they need to do to become compliant. This can make it difficult for organizations to implement the necessary security controls and practices.
- A lack of resources and expertise: Implementing the required security controls and practices can be resource-intensive and may require specialized expertise. Organizations may struggle to allocate the necessary resources and personnel to become CMMC compliant.
- Limited availability of certified third-party assessment organizations (C3PAOs) and Registered Practitioner Organizations (RPOs): In order to obtain CMMC certification, organizations must undergo a third-party assessment by a C3PAO. However, there are currently only a limited number of C3PAOs available, and the demand for their services is high. This can make it difficult for organizations to obtain the necessary certification in a timely manner.
- A lack of clarity and consistency in CMMC requirements: The CMMC is a new framework, and there may be some uncertainty and inconsistency in the requirements and guidance provided by the DoD. This can make it difficult for organizations to know exactly what to do to become compliant.
- The potential cost and disruption of becoming CMMC compliant: Implementing the required security controls and practices can be expensive and may require significant changes to an organization’s systems and processes. This can be disruptive and may require organizations to allocate significant resources to become compliant.
The Difference Between an RPO and C3PAO
Registered Practitioner Organizations (RPOs) are organizations that are registered with the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) Accreditation Body (AB) to provide training, and guidance and assist in implementing the CMMC requirements for organizations in the Defense Industrial Base (DIB). RPOs are not certified to conduct assessments of organizations to determine their compliance with CMMC requirements.
Third-Party Assessment Organizations (C3PAOs), on the other hand, are organizations that are certified by the CMMC AB to conduct assessments of organizations to determine their compliance with CMMC requirements. C3PAOs are responsible for conducting the third-party assessments that are required for organizations to obtain CMMC certification.
In summary, RPOs are organizations that provide training, and guidance assistance with implementations of the CMMC requirements, while C3PAOs are organizations that conduct assessments to determine an organization’s compliance with CMMC requirements. These are two different types of organizations that play different roles in the implementation of CMMC.
What is the Timeline for CMMC Compliance?
The timeline to become CMMC compliant will depend on several factors, including the level of compliance that an organization currently has and the level of CMMC certification it aims for.
In general, organizations will need to implement the required security controls and practices and undergo a certification process to demonstrate their compliance. This process can take some time and may require the assistance of certified third-party assessment organizations (C3PAOs).
Under the current “interim rule,” defense contractors that process, store, or create Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) are required to submit a NIST 800-171 self-assessment and submit their score until CMMC is fully implemented. If the government decides that a further assessment is necessary, defense contractors must grant access to their facilities, systems, and employees.
The CMMC is now Defense Department policy, and the interim rule lays out a timeline for compliance. An increasing number of contracts will formally require CMMC compliance in the Fall of 2025 when it will become a default requirement for all DoD contracts.
In the meantime, organizations should familiarize themselves with CMMC requirements under the interim rule and prepare to apply for certification at a later date. Due to the low number of C3PAOs currently available, most organizations will be unable to receive the third-party assessment required for CMMC certification at this time.
Why Prepare for CMMC with NOVO?
- Experience – Based on our years of experience implementing and assisting organizations with NIST regulations like SP 800-53 and SP 800-171 which form the basis of CMMC, NOVO can perform readiness assessments and even put in place the requirements to prepare you for an audit.
- Efficiency – Using industry-standardized platforms, NOVO is able to implement the CMMC requirements within your organization in as little as 5 business days.
- Expertise – NOVO provides information security solutions to public and private sector organizations. Our expert cyber security teams help our clients manage and secure their Information Technology (IT) and Operational Technology (OT) environments by providing vulnerability and penetration testing/assessments; governance, risk and compliance services (GRC) and security architecture review, design, and implantation services.
NOVO provides information security solutions to public and private sector organizations. Our expert cyber security teams help our clients manage and secure their Information Technology (IT) and Operational Technology (OT) environments by providing vulnerability and penetration testing/assessments; governance, risk and compliance services (GRC) and security architecture review, design and implantation services.

